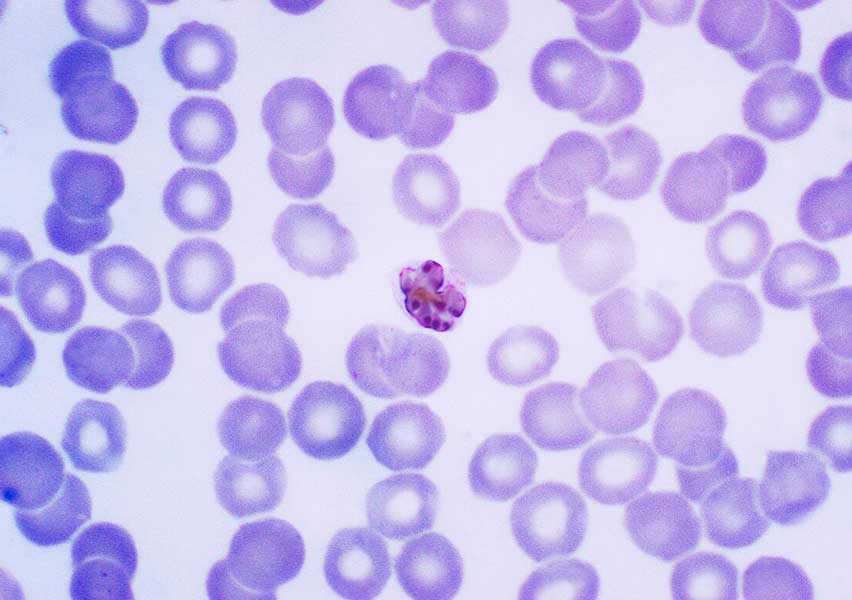
Plasmodium
Plasmodium spp. is a protozoan parasite belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa and the family Plasmodiidae. It is the causative agent of malaria, a potentially life-threatening disease with global distribution, particularly prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions.
Clinical features:
Malaria presents as an acute febrile illness. Symptoms usually begin after an incubation period of 7 to 30 days, depending on the species involved. The disease is characterized by cyclical episodes of high fever, chills, sweating, headache, muscle aches, nausea, and vomiting. Severe cases may progress to anemia, renal failure, pulmonary edema, cerebral malaria, and even death if left untreated.
Human malaria is primarily caused by five species: Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae, and P. knowlesi. Among these, P. falciparum is the most dangerous and prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa, while P. vivax is more common in Asia and Latin America. Relapses are possible with P. vivax and P. ovale due to dormant liver stages (hypnozoites).
Transmission occurs mainly through the bite of an infected female Anopheles mosquito, but may also happen via blood transfusion, organ transplantation, shared contaminated needles, or vertical transmission (from mother to child).
Diagnosis:
Malaria diagnosis relies on the identification of the parasite in peripheral blood, using Giemsa-stained thick and thin blood smears examined under a microscope. Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) and PCR may also be used depending on availability and context.
Speciation and quantification of parasitemia are critical for choosing the appropriate treatment and assessing risk.
Treatment:
Treatment depends on the Plasmodium species, disease severity, and region-specific drug resistance. For uncomplicated malaria, artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are recommended. In infections caused by P. vivax and P. ovale, primaquine is added to eliminate liver hypnozoites and prevent relapses.
For severe malaria, intravenous artesunate is the first-line treatment, followed by a full oral regimen.